-
Posts
578 -
Joined
-
Last visited
-
Days Won
138
Content Type
Profiles
Forums
Events
Everything posted by Ayesha
-
22m is very tall retaining wall. Even if you do it stepped, you can have a situation where the top wall is increase load on the lower wall, thus you aren't gaining any benefit out of the step. For such a wall, I would suggest that you engage geotechnical engineer and discuss with them about possible options like slope stability improvement etc.
-
This is a good question. I would suggest asking it to your professor and share the information here.
-

Calculating Partition Wall Load on Slab
Ayesha replied to Muhammad Munaf's topic in General Discussion
It helps with the checking. When you assign it, you can easily compare between structural dead weight and the weight of partitions. -
Diaphragm is explained above and you should be able to relate it based on the discussion.
-
-
Typically the Rigid End Zone (REZ)factor of 0 would assume a centerline based model which is typical of most basic analysis and should be accurate enough in general practice. Using a REZ of 1.0 assumes there are zero deformations within the area at the intersection of the columns and beams known as the "Panel Zone" (it is infinitely rigid). The "true" case lies somewhere in between and could be modeled using a rotational spring layouts (e.g. a scissors or krawinkler model). These factors and definitions are software dependent. Please see the software manual for more details.
-
Check ACI code. https://www.researchgate.net/post/How_can_I_implement_concrete_damage_plasticity_in_ABAQUS It depends on what you want out of the study. There are numerous outputs but depending upon the goal of the study, you can pick and analyze what interest you. Concrete InElastic Strain.pdf
-

Numerical Analyses of RC Beam Column joints in ABAQUS
Ayesha replied to Shahzad Khan's topic in General Discussion
Why do you want to do it in Abaqus? Why don't you analyse in ETABS or SAP? If you are a beginner and are not familiar with the theory of finite element analysis, it would be very challenging. May be read about FEM first and then use Abaqus.- 5 replies
-
- abaqus
- numerical analyses
-
(and 1 more)
Tagged with:
-
This would help:
-
For example, not talking about hinges here but you design of concrete beams, column in general is based on force control. You can also do a strain control design, where you assume strain in reinforcement and work your way back.Again, these examples are just to give you high level idea and not related to hinges.
-
There are a few but not easily available.
-

Rigid Raft with beams with different column dimension?
Ayesha replied to Abduldaniel's topic in Foundation Design
I am not familiar with BS, and I am not sure how tall the building it, but you should try to have beams equal or "larger" than the columns. The reason apart from strength and load transfer is that you want "easy reinforcement placement" which is very important especially at beam column locations where there can be too much congestion. I would advise you to revise your column size to match that of beam below. -
ELF is simple and quick. It was used at time when computers were not very common, so people went with it. Now, since every software can do Response Spectrum Analysis (RSA) , you are better off doing RSA.
-
You can go through the tutorial on this post:
-
That would provide you with the concrete strength of existing building at locations where you have taken the core, but other things that you need to confirm are if reinforcement provided matches the drawing and if the structure was built according to the drawings. You need to spot check reinforcement using PUNDIT for general elements and thoroughly check critical elements, check geometry, and use of existing building against the design drawing and also you need to know what code the existing building was designed too. After all that, you can evaluate the structure and then proceed with foundation checks.
-
I would suggest a method but my recommendation would be to have a geotechnical engineer get involved and let him suggest because structural engineers don't have that expertise. Several solutions can be implemented but the cheapest would be to cut back the soil at an angle that is safe. Other techniques that you can use are mechanical stabilization that can offer temporary improvement depending upon the extent of work that is carried out.
-
Force control means behavior would be determined based on the amount of force specified and displacement control means that the behavior is determined based on the amount of displacement specified.
-
This is sometimes due to pattern live load. This has been discussed in detail and you can check the solution in the links posted below.
-

Calculating Partition Wall Load on Slab
Ayesha replied to Muhammad Munaf's topic in General Discussion
Can you explain more. Are you having problems "calculating" the load or "applying it" Here is the traditional way to calculate the load. Calculate the volume of the partition wall and multiply by density of material. That will give you the total load of the partition wall. Divide it by the length of wall and you have a linear load that you can apply using dummy beam. -
Because that might be causing your main beam to act as a cantilever beam and transfer a bigger moment to column. See deflected shape and it will confirm the hypothesis.
-
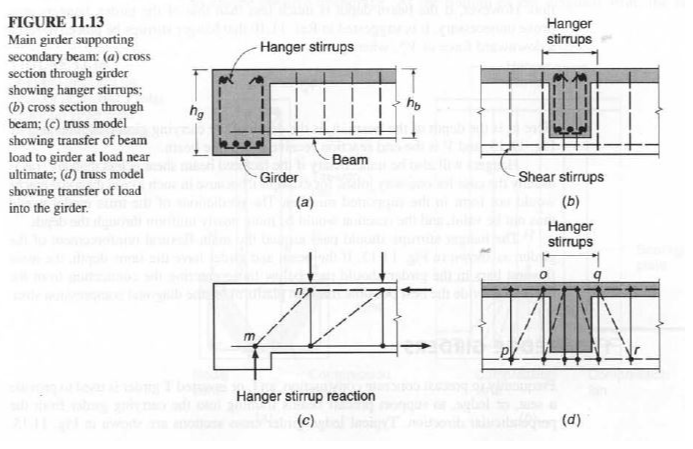
Requirement for hanger bars and stirrups can be checked through strut and tie . Here is an excerpt from Design of Concrete Structures" by Arthur Nilson, David Darwin Charles Dolan (and illustration attached) on the same topic providing additional info :
-
Do you want to check the vibration because of human activity or is there a machine that is operating?
- 10 replies
-
- floor vibrations
- vibrations
-
(and 1 more)
Tagged with:
-
If you don't have rebar, then monolithic connection means nothing. You don't have to break the main beam.
-
All kind of piles (I don't know what sand pile is) can take earthquake if they are designed for it. For liquefaction, piles installed by hammering would be better as you will compact the ground as you install them (like driven steel piles). Expert opinion should be taken from geotechnical engineer as this is more geotech domain.
-
You can release all the moment and let secondary beam behave as pinned end. For reinforcement detailing, use hanger bars.